Anxiety is a natural emotional response to stress or perceived threats, commonly experienced by individuals in various stages of life. While mild anxiety can serve as a motivational force or a warning signal for danger, persistent or excessive anxiety can lead to a wide range of psychological, emotional, physical, and social challenges. In today’s fast-paced and pressure-driven world, anxiety disorders are becoming increasingly common, affecting millions globally. This article delves into the concept of anxiety, its causes, symptoms, and the multiple disadvantages it brings to individuals and society.
Understanding Anxiety
Anxiety is characterized by feelings of tension, worried thoughts, and physical changes like increased blood pressure, rapid heartbeat, and restlessness. While short-term anxiety is considered a natural part of life, chronic anxiety is classified as a disorder and can severely interfere with daily functioning. The most common forms include:
- Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
- Social Anxiety Disorder
- Panic Disorder
- Specific Phobias
- Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
- Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Each of these disorders affects people differently and requires specific therapeutic approaches.
Causes of Anxiety
There is no single cause of anxiety. It typically results from a complex interplay of factors, including:
- Genetics: Family history can increase susceptibility.
- Brain Chemistry: Imbalances in neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine.
- Environmental Factors: Stressful life events, trauma, or abuse.
- Medical Conditions: Chronic illnesses or substance withdrawal.
- Personality Traits: People with low self-esteem or perfectionist tendencies are more prone.
Symptoms of Anxiety
Anxiety affects both the mind and the body. Some common symptoms include:
- Constant worrying or fear
- Irritability or mood swings
- Muscle tension and headaches
- Trouble sleeping or insomnia
- Difficulty concentrating
- Racing thoughts
- Rapid breathing and heart rate
- Gastrointestinal problems
These symptoms can escalate over time, interfering with both personal and professional life.
Disadvantages of Anxiety
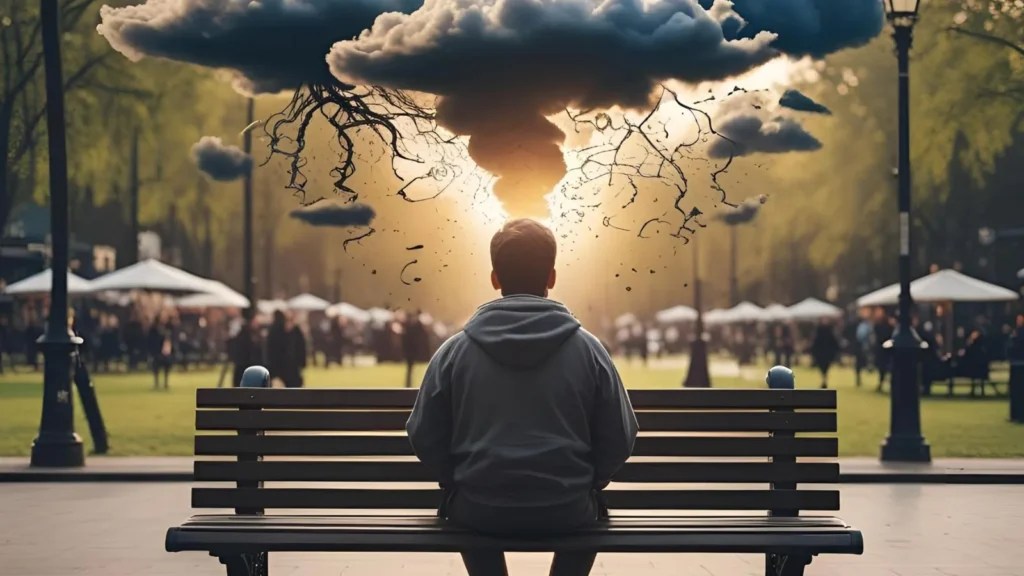

While anxiety may start as a manageable condition, its disadvantages can multiply if left untreated.
1. Emotional Exhaustion
Anxiety drains emotional energy. The constant fear of what might go wrong leaves individuals feeling overwhelmed, frustrated, and helpless. Over time, this emotional burden can develop into depression, burnout, or emotional numbness.
2. Poor Academic and Professional Performance
Anxiety can impair memory, focus, and decision-making skills. Students may struggle to study or take exams, while professionals may find it difficult to meet deadlines, handle pressure, or attend meetings. This can hinder personal growth and career advancement.
3. Disrupted Relationships
Anxiety often causes individuals to be overly self-conscious, irritable, or distant. This affects friendships, romantic partnerships, and family dynamics. Loved ones may find it hard to understand the anxiety sufferer’s needs, leading to tension or emotional disconnect.
4. Physical Health Problems
Chronic anxiety affects the body as much as the mind. It is associated with numerous physical ailments such as:
- High blood pressure
- Heart disease
- Gastrointestinal issues (e.g., IBS)
- Weakened immune system
- Headaches and chronic fatigue
These symptoms can become chronic if anxiety is not managed properly.
5. Sleep Disorders
Many anxiety sufferers experience difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep due to racing thoughts or physical discomfort. Over time, lack of sleep weakens cognitive function, immune defense, and emotional stability.
6. Panic Attacks
Panic attacks are sudden, intense surges of fear accompanied by physical symptoms like sweating, chest pain, and dizziness. They can happen without warning and leave a lasting emotional impact, increasing the fear of future episodes.
7. Social Isolation
Social anxiety leads individuals to avoid gatherings, speaking in public, or even leaving the house. This isolation can worsen feelings of loneliness, guilt, and depression, creating a vicious cycle that is difficult to break.
8. Low Self-Esteem
Chronic anxiety often leads to self-doubt, negative self-talk, and a lack of confidence. People may feel inadequate or fear judgment, which limits their willingness to take risks or try new things.
9. Substance Abuse
In an attempt to numb their feelings, some individuals resort to alcohol, smoking, or drugs. While these may provide short-term relief, they usually worsen anxiety in the long run and increase the risk of addiction and health complications.
10. Decreased Quality of Life
Whether it’s avoiding social situations, missing job opportunities, or declining health, the overall impact of anxiety significantly reduces a person’s enjoyment and satisfaction with life. Everyday tasks become sources of dread rather than joy.
Long-Term Consequences
When anxiety goes untreated for long periods, the disadvantages deepen:
- Chronic Disorders: Like hypertension, ulcers, and migraines
- Impaired Childcare: Parents with anxiety may struggle with patience, consistency, and emotional support
- Disability: Severe anxiety may limit a person’s ability to work, study, or socialize, leading to disability claims
- Economic Burden: Both personal (medical costs, job loss) and societal (healthcare systems, lost productivity)
The Importance of Early Intervention
One of the most critical disadvantages of anxiety is how easily it goes unnoticed or untreated. Many people either dismiss their symptoms or feel too ashamed to seek help. However, early intervention can prevent long-term damage.
Effective treatment options include:
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): Helps change negative thought patterns
- Medication: Such as SSRIs or anti-anxiety drugs, under medical supervision
- Mindfulness and Relaxation Techniques: Like meditation, deep breathing, and yoga
- Lifestyle Changes: Exercise, sleep hygiene, and a healthy diet
- Support Groups: Sharing experiences with others who understand can be healing
Conclusion
Anxiety is more than just a feeling of nervousness—it is a serious mental health condition with far-reaching disadvantages. It affects how individuals think, feel, behave, and interact with the world. From poor health and broken relationships to career limitations and emotional suffering, the impact of anxiety can be life-altering. However, with awareness, compassion, and the right treatment, anxiety can be managed, and individuals can reclaim control over their lives.